
What is Ulcerative Colitis (UC)?
UC belongs to a larger group of illnesses called inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). UC is a chronic—ongoing, long-term—condition where inflammation in the large intestine (colon and rectum) can lead to symptoms over time. With UC, your overactive immune system causes inflammation that damages your colon lining.
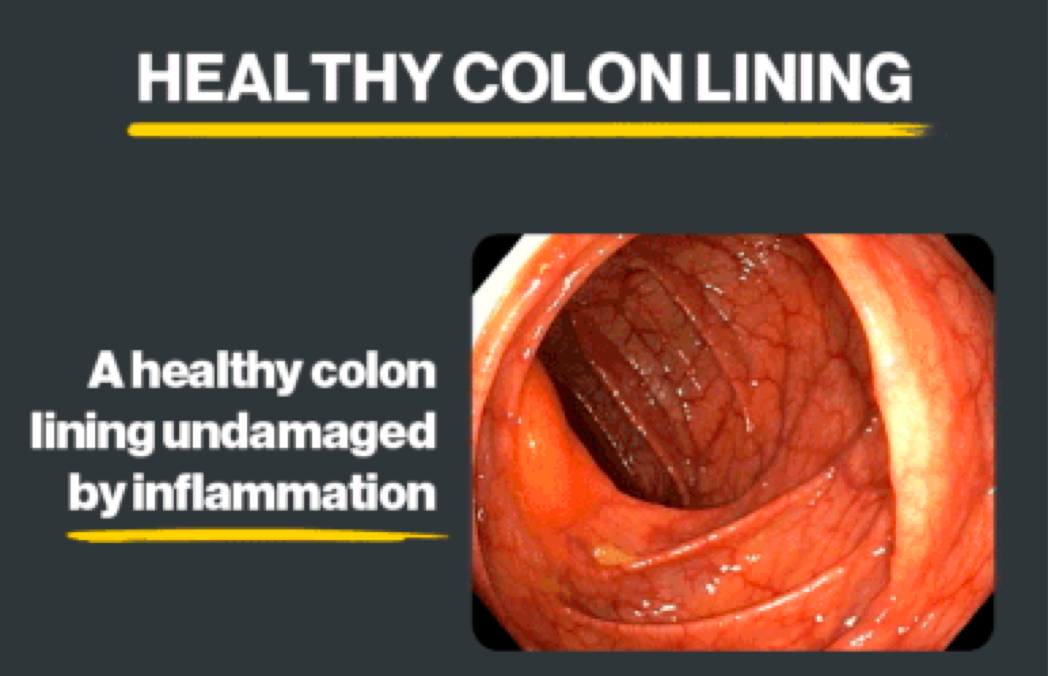
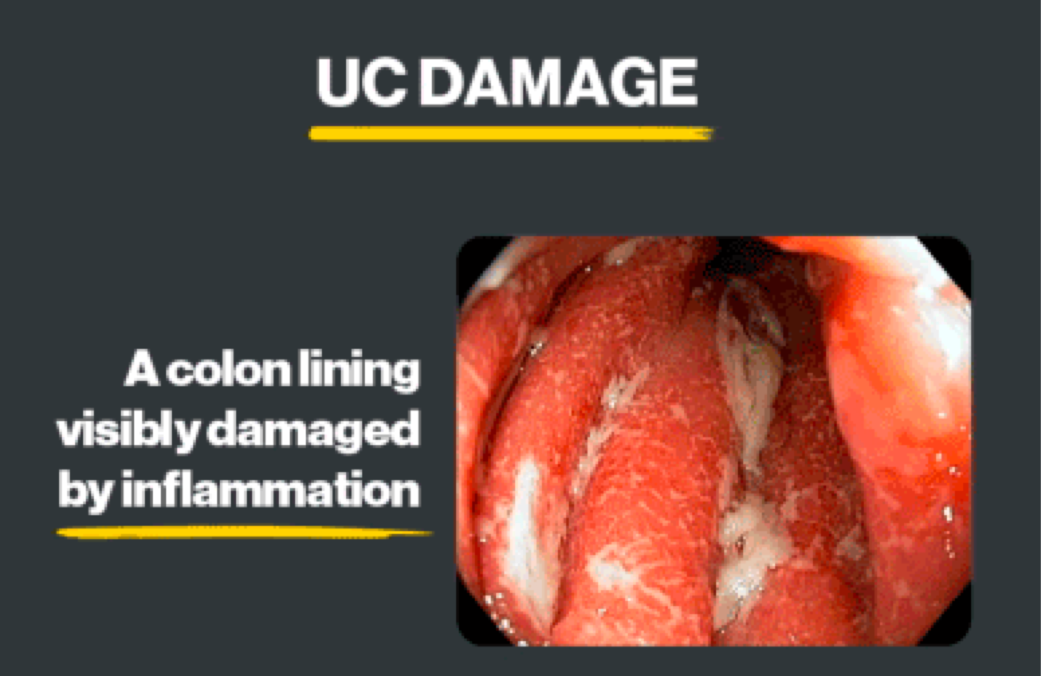
Symptoms and Signs of UC
UC symptoms can be unpredictable and affect each person differently. Symptoms may present as particularly active at times (flare-ups or relapses), mild and more manageable, or none at all (remission). However, if not managed effectively, it can lead to other complications, and some patients may require hospitalisation and eventually surgery.
Some common UC symptoms include:
Bloody stools
Sudden accidents
Abdominal pain (tummy/puku area)
Frequent bathroom trips
Fatigue
What is the cause of UC?
While the exact cause of UC is unknown, it can be influenced by many different factors, including a person's immune system, genetics, or other environmental factors.
In UC:
- Your immune system mistakenly harms healthy cells in the inner lining of the large intestine, or colon.
- The overactivity of the immune system causes excess inflammation in your colon.
- Too much inflammation can lead to colon damage and UC symptoms.